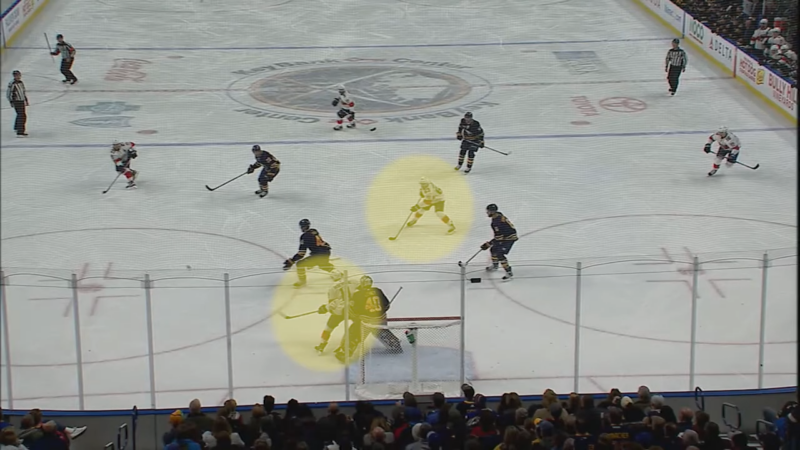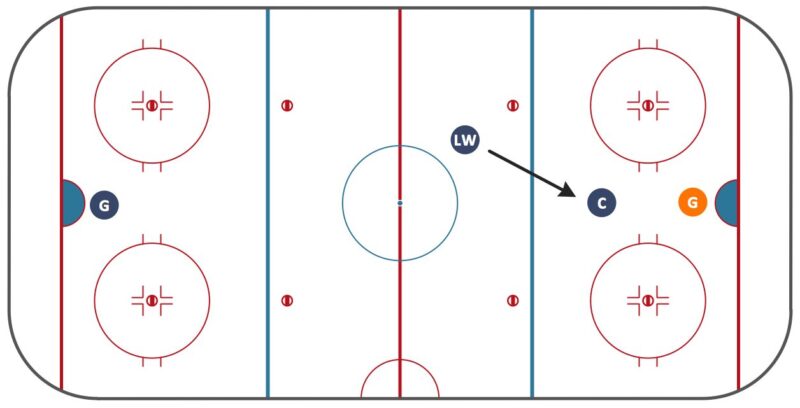
Think of the hockey rink split into three main parts: one for each team’s defensive zone and the middle part, which is neutral. The important line for offsides is the blue line that separates the neutral area from the attacking zone.
Here’s the deal: when a team is moving into the attacking zone to score, the puck has to cross that blue line before any player on the attacking team does. If a player zooms in before the puck does, the play gets whistled down for offsides. It’s like saying, “Hey, you’re too eager; let the puck in first!”
Coaches and players must constantly be aware of their positioning relative to the puck and the blue line. This awareness influences how teams set up their attacks and defenses, making offside knowledge not just a rule to follow but a strategic tool to exploit.

Why is this rule important?

The offsides rule in hockey is straightforward yet vital for the game’s integrity. It dictates that a player cannot enter the offensive zone before the puck. A player is considered offside if they cross the blue line into the offensive zone before the puck.
This rule is designed to prevent players from gaining an unfair advantage by waiting near the opponent’s goal. The rule encourages more skillful play, requiring teams to enter the offensive zone as a unit. The offside rule has evolved over the years. Initially, the rule was more restrictive, with players unable to pass the puck forward across lines.
Over time, to encourage more dynamic play and scoring, the rule was relaxed to its current form. This evolution reflects the sport’s growth and the continuous effort to balance fairness with excitement. The changes in the offsides rule mirror hockey’s evolution. As the game became faster and more skill-oriented, the rule adapted.
These adaptations have made the game more appealing to spectators, as they lead to a faster-paced game with more scoring opportunities, while still maintaining a strong strategic element.
How does it affect the game?
This rule requires precise timing and coordination among team members, as they maneuver to advance into the offensive zone without committing an offsides violation. Player positioning in relation to offsides is a game of precision. Forwards, in particular, must carefully time their movements to avoid crossing the blue line too soon.
The fundamental principle is simple: a player cannot enter the offensive zone before the puck. For a player to be onside, the puck must cross this line before any player of the attacking team.
However, controversies around offsides calls, especially in crucial game moments, can also lead to calls for rule clarifications or changes, reflecting the rule’s significant impact on the outcome of games.
When a team is deemed offside, it results in immediate game impacts and influences long-term team strategy and player behavior.
| Aspect | Impact |
|---|---|
| Faceoff | Play is stopped, and a faceoff is conducted near the blue line |
| Loss of momentum | Disrupts game flow allows the defending team to regroup |
| Potential scoring opportunity lost | Well-timed entry into the offensive zone forfeited due to offsides |
Long-term effects on team strategy
Coaches and players often adapt their strategies based on offsides tendencies, aiming for more precise entries. Players must develop discipline in their positioning and timing to avoid costly offsides infractions.
Also, psychological aspects come into play, as defenders may attempt to bait offensive players into offsides situations.
Why good linesman is essential?
- Linesmen position themselves along the blue line to have the best view of the play.
- They must blow the whistle promptly when offsides occurs, halting play.
- Linesmen work in tandem with the referee to make precise calls, often through hand signals.
- The speed of the game can make offsides calls challenging, but linesmen are trained to keep up with the play.
- In some cases, video review technology is used to ensure the correctness of an offsides call.
- Experienced linesmen develop an innate sense for offsides situations through years of officiating.
Training is crucial for players to avoid it!
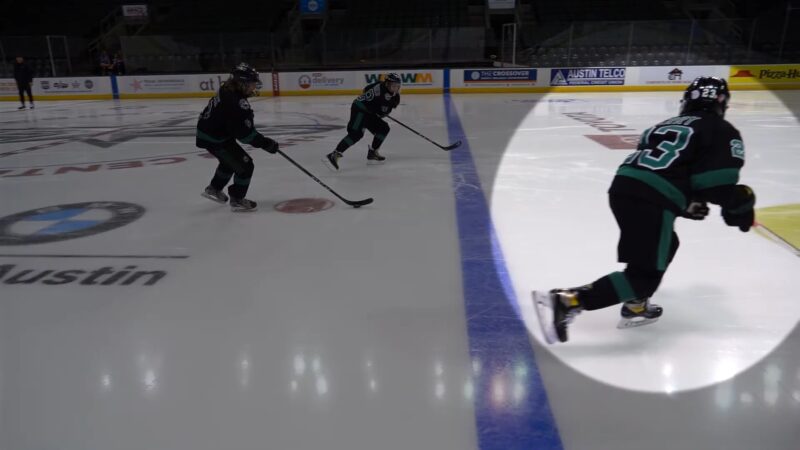

Psychologically, the offsides rule can be used as a tactical tool. Teams often employ it to disrupt the rhythm of their opponents or to bait them into making mistakes. This aspect adds a layer of complexity to the game, as teams must continually adapt their strategies based on their opponents’ tendencies regarding offsides.
Offsides-focused training is a key part of player development, from youth leagues to professional teams. Coaches design specific drills to improve players’ understanding and execution of offsides strategies, ensuring they can effectively navigate this rule during high-pressure situations. Players must not only be fast and skilled with the puck but also possess a keen sense of spatial awareness and timing.
Players who can read the game well and anticipate movements tend to excel in navigating the complexities of the offsides rule.
Related Posts:
- How Long Is the Average Hockey Game? - Puck Drops,…
- Panthers Secure Victory in Game 5, Lightning Eliminated
- The Thrill of the Ice: Navigating Sports Betting in…
- What Is a Powerplay in Hockey? Strategies, Rules,…
- Hockey Skates vs. Figure Skates - What is the Difference?
- Why Do They Let Hockey Players Fight? Is Fighting Allowed?